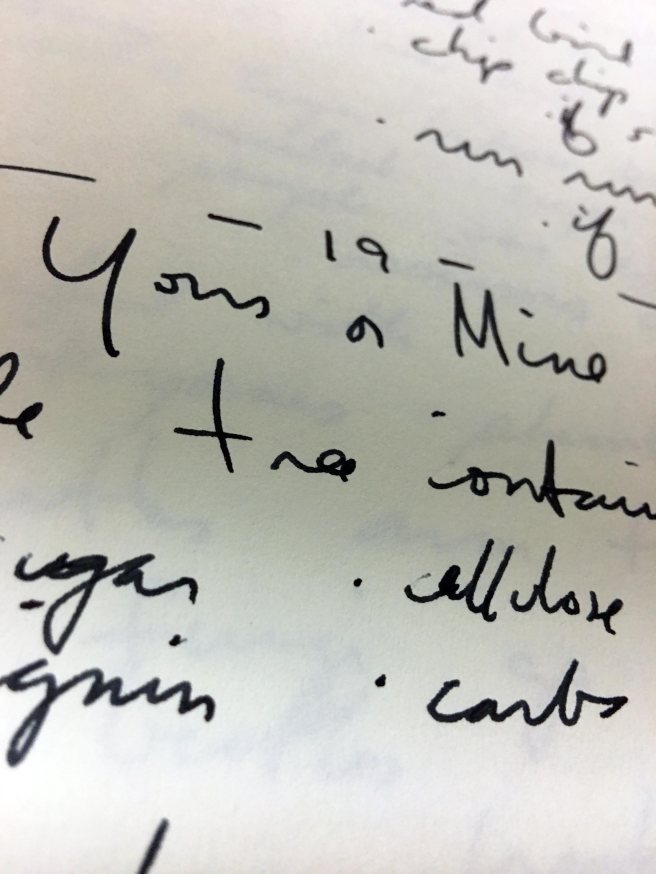
Peter Wohlleben’s The Hidden Life of Trees
Page numbers in parentheses. Italics are my own questions of the text.
Chapter 17 Notes Chapter 18 Notes
Chapter 14 Notes Chapter 15 Notes Chapter 16 Notes
Chapter 13 Notes Chapter 12 Notes Chapter 11 Notes
Chapter 10 Notes Chapter 9 Notes Chapter 8 Notes
Chapter 7 Notes Chapter 6 Notes Chapter 5 Notes
Chapters 3 & 4 Notes Chapter 2 Notes Foreword, Introductions, and Chapter 1 Notes
Chapter 19 – Yours and Mine
this chapter outlines all of the ways trees get attacked throughout their lifetime
single tree contains millions of calories (114)
• sugar • cellulose • lignin • carbs
• woodpecker
• beak and head muscles absorb impact
• sapsuckers drill dotted line in the thinner branches
• trees must tolerate
• aphids
• attach mouth sucking parts to veins in leaves and needles
• sap runs right through them out into very large droplets – ‘honeydew’
• very little protein
• expel mostly carbs and sugar
• specialized aphids for each tree species
• wooly beetle scale (115)
• attacks bark
• envelop trunks with silvery white wool
• festering wounds in bark
• take a long time to heal
• if fungi get in tree can die
• ladybug larvae (116)
• devour aphids
• forest ants
• eat honeydew right off aphid backsides
• ants protect the aphids
• honeybees
• make dark forest honey out of honeydew
• gall midges and wasps
• larvae feed on leaves
• saliva reprograms leaves to grow into casing, also called a gall
• leaves fall to the ground, and the midge pupates and hatches (117)
• caterpillars
• eat leaves and needles in their entirety
• trees stripped of leaves by june
• tree mounts a comeback
• however after 2 – 3 years in a row of attacks, trees can die
• bird cherry (118)
• leaves contain nectar gland
• nectar for ants
• ants rid the bird cherry of caterpillars
• ants will farm aphids (119)
• barb beetle
• single beetle mounts attack
• if successful calls in reinforcements
• or tree kills first beetle
• cambrium
• active layer between bark and wood
• succulent • sugar • minerals
• people can eat
• tastes like resinous carrot
• spruce
• defend with
• terpenes, phenols
• can kill beetles
• beetles arm themselves with fungi
• fungi go in ahead of the beetles
• fungi moves faster than drilling beetles
• fungi breaks down defense chemicals into harmless substances
• large herbivores (120)
• not much greenery on forest floor
• leaves of trees in crown too high
• not many deer in forests
• old tree falls over
• light reaches forest floor for a few years
• wild flowers and grasses grow
• light = sugar
• trees bud (121)
• trees have to grow fast enough that the large herbivores can’t get to them
• honey fungus mushroom
• fruiting body on tree stumps in fall (122)
• mycelium
• force their way into roots
• steal from cambrium
• eat through wood
• causes host wood to rot
• pinesap
• same family as blueberries
• can’t photosynthesize
• taps into link between fungi & roots
• small cow wheat
• similar to pinesap
• male deer
• rub the velvet off antlers using young trees
• uses the uncommon local tree for some reason why?
• trees equal less than 4 inches
• grass is a rarity in a natural forest
• deer forced into forests
• sneak out at night
• eat tree bark in desperation
• tree is full in summer
• bark easy to peel
• winter
• deer can only peel off chunks
• trees in natural woods can survive this
• tough because of slow growth
• commercial forests
• trees grow quickly
• contain a great deal of air
• room for fungi
• snap in middle age


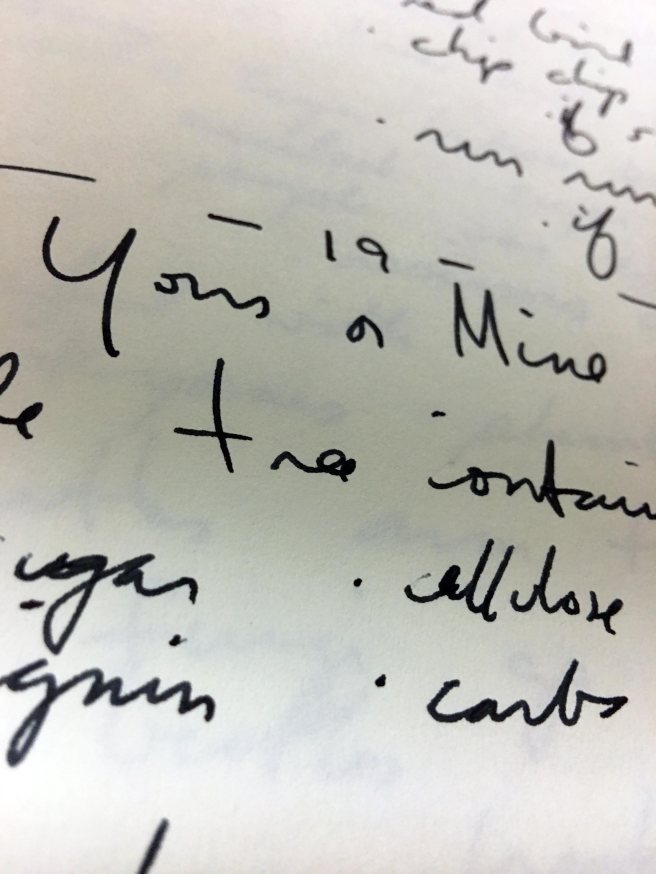
 Peter Wohlleben’s The Hidden Life of Trees
Peter Wohlleben’s The Hidden Life of Trees